What does it mean when your probability plot has clusters
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
If you’re interested in statistics and data analysis, then you’ve probably heard of Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient. This statistical tool can help you analyze data and find correlations that may not be immediately apparent. In this post, we’ll dive into what Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient is, why it’s important, and how you can use it to your advantage.
If you’ve ever worked with complex data sets, then you know how challenging it can be to uncover meaningful insights. Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient can help you find patterns and connections between different variables in your data, even when those connections are not immediately apparent. By using this tool, you can gain a more nuanced understanding of the relationship between different variables and better predict future outcomes.
At its core, Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient is a measure of the strength of the relationship between two variables. It’s expressed as a number between -1 and 1, with -1 indicating a perfect negative correlation, 0 indicating no correlation, and 1 indicating a perfect positive correlation. Essentially, it tells you how closely two variables are related, and in what direction.
So how exactly can you use Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient? One of the primary use cases is for predicting future outcomes based on past data. By analyzing the correlation between different variables, you can make more accurate predictions about what might happen in the future. Additionally, it can help you identify areas where you may need to make changes in order to achieve your goals more effectively.
Understanding Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient
When you’re trying to understand Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient, it can be helpful to think of it in terms of a scatter plot. A scatter plot is a graphical representation of two variables, with one plotted along the x-axis and the other along the y-axis. If there’s a strong correlation between the two variables, then the points on the scatter plot will cluster together in a specific pattern. The closer the points are to each other, the stronger the correlation.
For example, let’s say you’re analyzing data related to customer satisfaction at a restaurant. You might use Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient to analyze the relationship between the quality of the food and the overall satisfaction rating. If there’s a strong correlation between these two variables, then you might be able to improve overall satisfaction by focusing on improving the quality of the food.
Using Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient in Real Life
I’ve personally used Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient to help businesses understand their customer data. By analyzing the correlation between different variables, we were able to identify areas where they needed to make changes in order to achieve their goals. In one case, we found that there was a strong correlation between customer satisfaction and the speed of the checkout process. By streamlining the checkout process, the business was able to improve overall satisfaction and increase revenue.
How to Calculate Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient
Calculating Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient is a bit more complicated than just plugging numbers into a formula. However, there are many statistical software programs available that can help you do this quickly and easily. Some popular options include R, SAS, and SPSS.
Interpreting Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient
When interpreting Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient, it’s important to keep in mind that correlation does not necessarily imply causation. Just because two variables are correlated, that doesn’t mean that one causes the other. Additionally, a correlation of 0 does not necessarily mean that there is no relationship between two variables–it just means that there is no linear relationship.
Applying Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient to Your Data
If you’re interested in using Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient to analyze your own data, there are a few key steps you’ll need to follow. First, you’ll need to identify the variables you want to analyze and make sure you have accurate data for each of them. Then, you’ll need to calculate the correlation coefficient using a statistical software program. Finally, you’ll need to interpret the results and determine what they mean for your specific situation.
Question and Answer about Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient
Q: What is a perfect correlation coefficient?
A: A perfect correlation coefficient is 1.0 or -1.0, indicating a strong positive or negative correlation, respectively.
Q: How do you interpret a correlation coefficient of zero?
A: A correlation coefficient of zero suggests that there is no linear relationship between the two variables, but there may still be other types of relationships.
Q: Can you use Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient to make predictions?
A: Yes, Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient can be used to make predictions based on past data. However, it’s important to keep in mind that correlation doesn’t necessarily imply causation, and there may be other factors affecting the relationship between variables.
Q: What are some limitations of Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient?
A: Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient only measures linear relationships, and it can be affected by outliers and other factors that may distort the data.
Conclusion of Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient
Probability Plot Correlation Coefficient is a powerful statistical tool that can help you analyze complex data sets and uncover hidden insights. By understanding the correlation between different variables, you can make more informed decisions and better predict future outcomes. However, it’s important to keep in mind the limitations of this tool and interpret the results carefully, so that you don’t draw incorrect conclusions or make poor decisions based on faulty data.
Gallery
Normal Probability Plot - What You Need To Know For A Six Sigma Exam
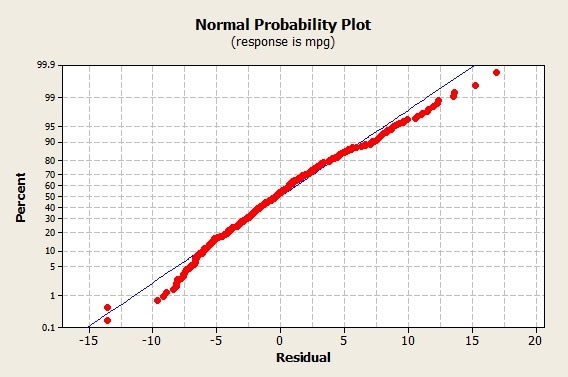
Photo Credit by: bing.com / probability axis
Data Visualization - Formula For Probability-probability Plot - Cross

Photo Credit by: bing.com / probability plot normal minitab distribution data skew formula chart axis positions calculate why
Probability-plot Correlation Coefficient (^ R) For The Warm Season

Photo Credit by: bing.com / probability coefficient correlation streamflows
What Does It Mean When Your Probability Plot Has Clusters?
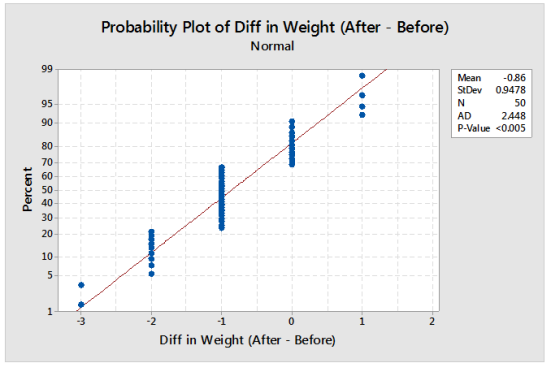
Photo Credit by: bing.com / probability plot patient weight clusters mean does when surgery before after above based
Normal Probability Plot: Definition, Examples
Photo Credit by: bing.com / plot probability normal normality data assumption sample approximately straight line distributed normally test definition examples diagonal excel statistic order gif