Solved 17 the maximum probability of committing a type i
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
In statistics, committing a Type I error is sometimes inevitable, but it can have serious consequences. Have you ever wondered about the probability of committing a Type I error? Read on to find out all you need to know about this statistical error.
Potential Pain Points
If statistical significance is important to your research or work, then understanding Type I errors is crucial. Errors can lead to drawing incorrect conclusions and taking inappropriate actions. This could result in missed opportunities or wasted resources.
Target of Probability of Committing a Type I Error
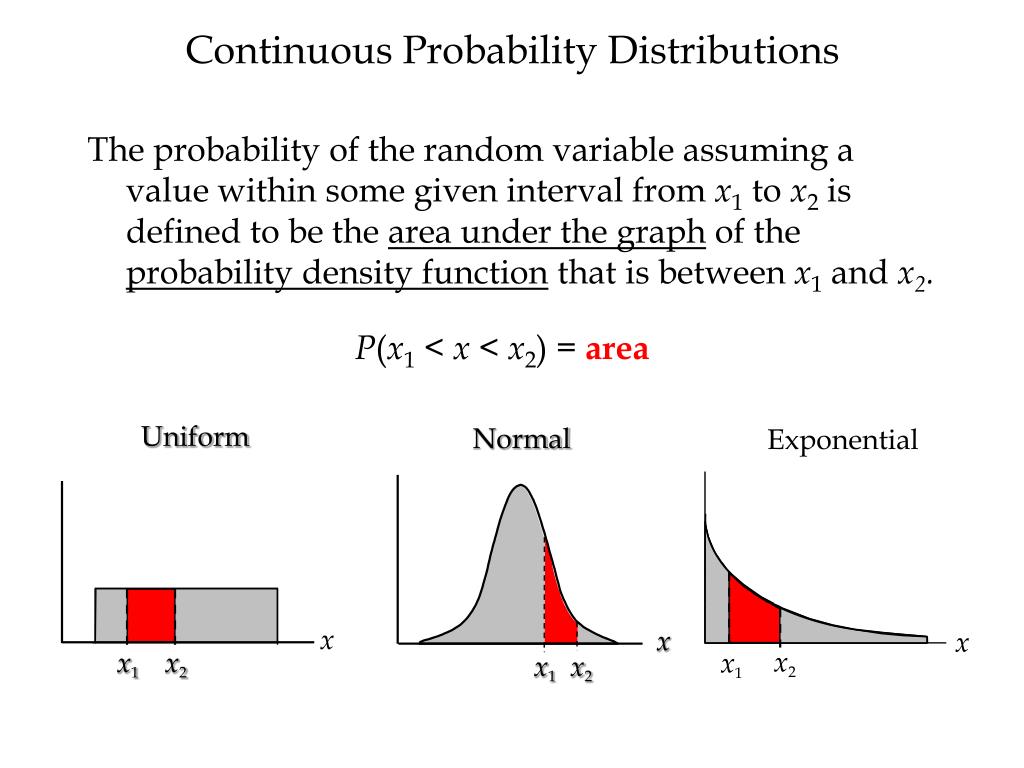
The probability of committing a Type I error is the alpha level you set before performing a statistical test to determine significance. This alpha level is typically set at 0.05, which means there is a 5% probability of rejecting the null hypothesis (i.e., concluding that there is a significant effect) when, in reality, there isn’t one.
Summary of Main Points
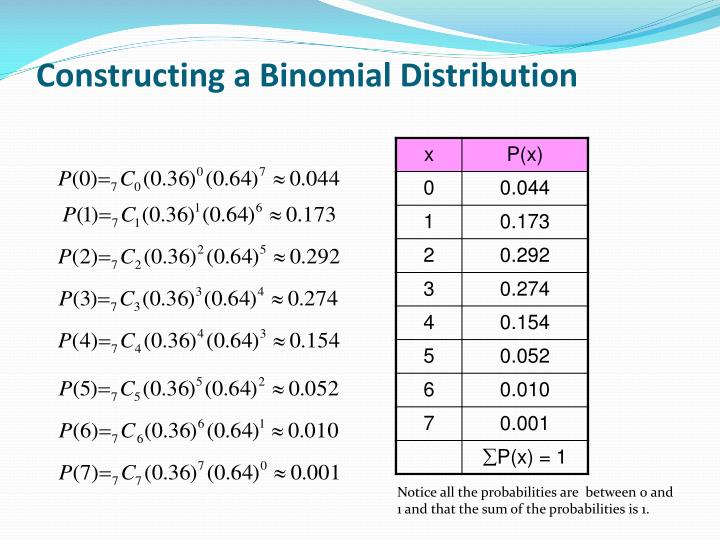
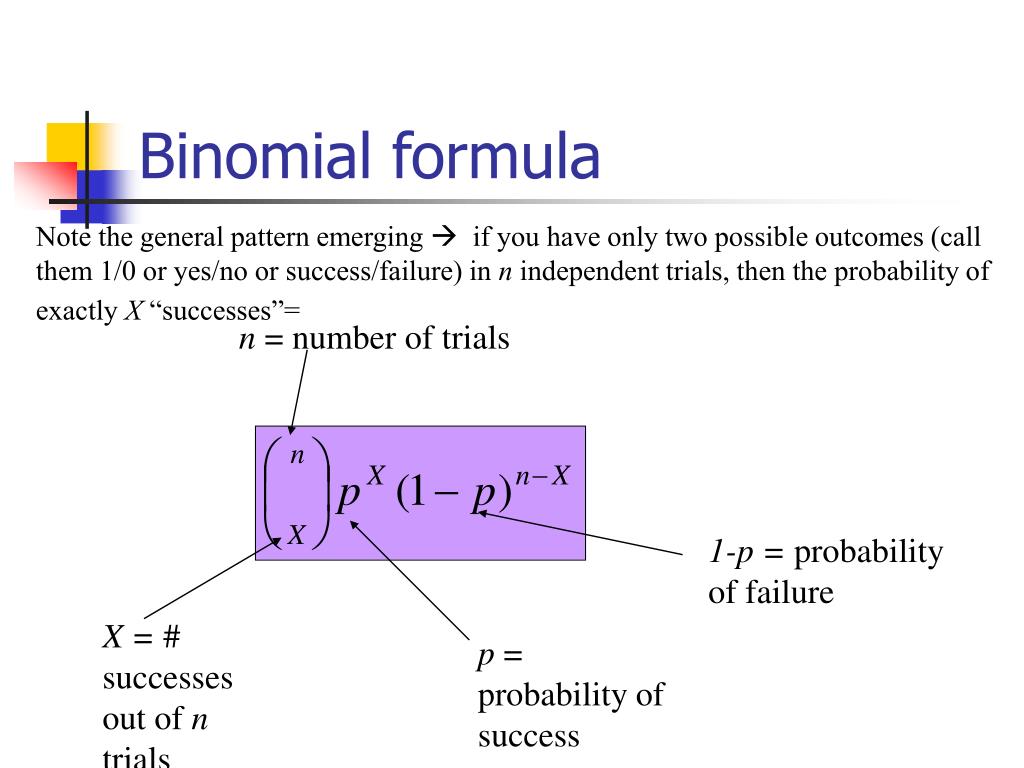
Committing a Type I error is when you reject the null hypothesis when it is actually true. The probability of committing a Type I error is the alpha level you set before conducting a statistical test. The standard alpha level is 0.05, and errors can have serious consequences.
My Personal Experience with Probability of Committing a Type I Error
As a researcher, minimizing Type I errors is always a priority. In one study I conducted, we set our alpha level at 0.01 to ensure we were more cautious in rejecting the null hypothesis. It ended up being a good decision, as we were able to detect a significant effect that may have been overlooked otherwise.
 Common Causes of Probability of Committing a Type I Error
Common Causes of Probability of Committing a Type I Error
The most common cause of Type I errors is not understanding the test you are performing and the significance level you have set. Other causes include small sample sizes, multiple testing, and bias in the data analysis.
### How to Avoid Probability of Committing a Type I Error
To avoid Type I errors, it is essential to understand the statistical test you are using and the significance level you have set. It is also important to ensure you have a large enough sample size to detect significant effects. Additionally, performing sensitivity analyses can help identify the robustness of your findings.
 #### The Relationship between Probability of Committing a Type I Error and Type II Error
#### The Relationship between Probability of Committing a Type I Error and Type II Error
When the probability of committing a Type I error decreases, the probability of committing a Type II error increases. This trade-off is known as the power and type I error rate dilemma. Thus, it is crucial to consider both errors when interpreting statistical results.
FAQs About Probability of Committing a Type I Error
What is the difference between Type I and Type II errors? Type I errors occur when you reject the null hypothesis when it is actually true. Type II errors occur when you accept the null hypothesis when it is actually false.
What is the standard alpha level used in statistical tests? The standard alpha level is 0.05, meaning there is a 5% chance of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true.
What are some common causes of Type I errors? Common causes of Type I errors include not understanding the test being performed, small sample sizes, multiple testing, and bias in data analysis.
How can you avoid Type I errors in statistical tests? To avoid Type I errors, it is essential to understand the test being performed, have a large enough sample size, and perform sensitivity analyses to test the robustness of findings.
Conclusion of Probability of Committing a Type I Error
Probability of committing a Type I error is an important concept in statistics that can have serious consequences if not understood correctly. By setting the appropriate alpha level, understanding the statistical test being performed, and increasing sample size, researchers can reduce the likelihood of making Type I errors that could lead to incorrect conclusions and wasted resources.
Gallery
Solved 17. The Maximum Probability Of Committing A Type I | Chegg.com
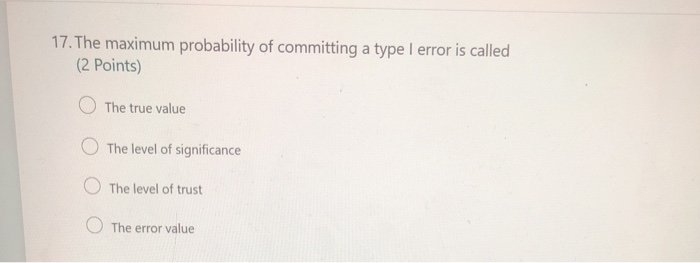
Photo Credit by: bing.com / committing probability maximum significance points transcribed
Answered: 1. What Type Of Error Occurs If You… | Bartleby

Photo Credit by: bing.com / error occurs
Hypothesis Testing (w/ 21 Step-by-Step Examples!)
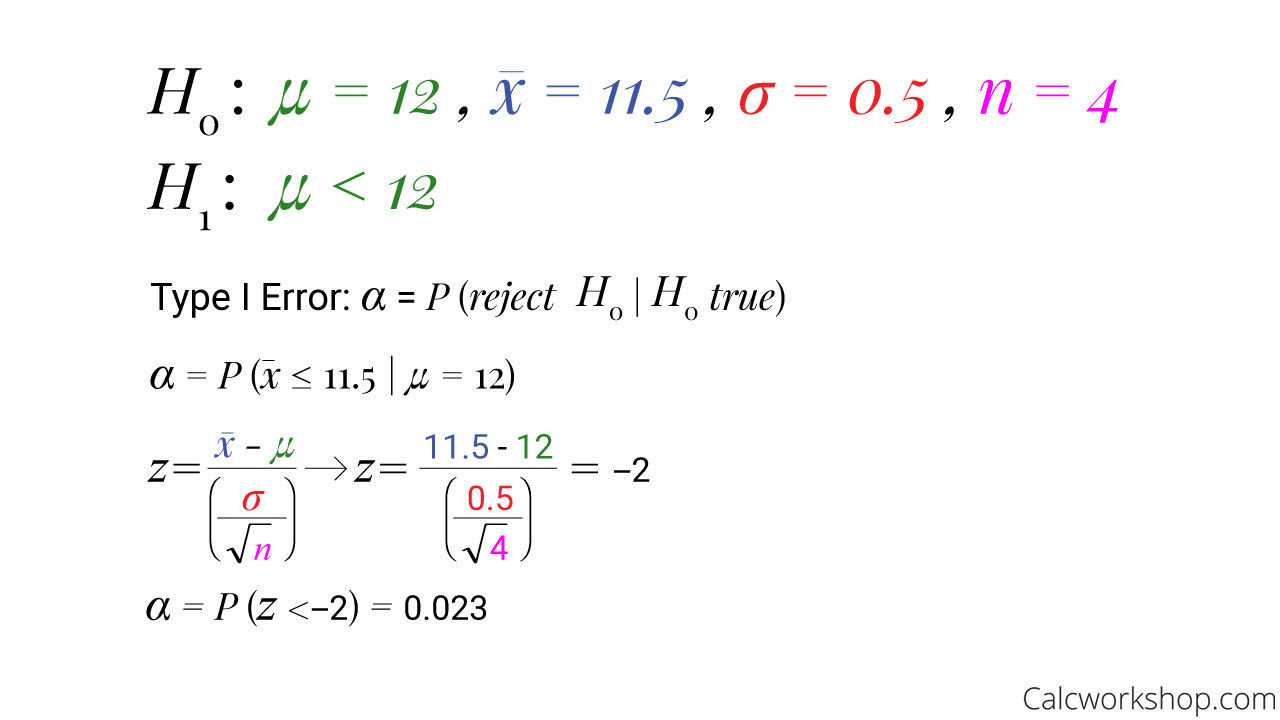
Photo Credit by: bing.com / error type example hypothesis testing step examples
Statistics - How Do I Find The Probability Of Committing A Type II

Photo Credit by: bing.com / error probability type find committing ii statistics
Solved 1. The Probability Of Committing A Type I Error Is | Chegg.com
Photo Credit by: bing.com /