Mr rouche s maths conditional probability trees
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Are you struggling with understanding Conditional Probability Example Problems? Do you find yourself getting confused when it comes to calculating probabilities based on multiple events? If so, you’re not alone. Many students struggle with Conditional Probability Example Problems, but with a little practice and some helpful tips, you can improve your understanding and solve these problems with ease.
Conditional Probability Example Problems are tricky because they involve calculating probabilities based on multiple events. This means that you need to consider the probability of Event A happening given that Event B has already occurred. This can be confusing, and many students get stuck on these types of problems.
If you’re struggling with Conditional Probability Example Problems, don’t worry. The key to solving these problems is to understand the concepts behind them. First of all, you need to understand what conditional probability means. Conditional probability is the probability of one event occurring given that another event has already occurred.
In summary, Conditional Probability Example Problems involve calculating probabilities based on multiple events. To solve these problems, you need to understand the concepts behind them and practice applying them to different scenarios.
Examples of Conditional Probability Example Problems
One example of Conditional Probability Example Problems is rolling two dice. What is the probability of rolling a 6 on one die and a 4 on the other die given that the sum of the two dice is 10? To solve this problem, you need to calculate the probability of rolling a 6 given that the sum of the dice is 10. Then, you need to calculate the probability of rolling a 4 given that the sum of the dice is 10. Finally, you need to multiply these probabilities together to get the answer.
Another example of Conditional Probability Example Problems is drawing cards from a deck. What is the probability of drawing a spade given that the card is black? To solve this problem, you need to calculate the probability of drawing a spade and the probability of drawing a black card. Then, you need to calculate the probability of drawing a spade given that the card is black by dividing the probability of drawing a spade and a black card by the probability of drawing a black card.
Tips for Solving Conditional Probability Example Problems
One tip for solving Conditional Probability Example Problems is to use a probability tree. This can help you visualize the different outcomes and calculate the probabilities more easily. Another tip is to break the problem down into smaller parts. This can make it easier to calculate the probabilities of each event and combine them to get the final probability.
Using a Probability Tree
A probability tree is a visual way to represent the different outcomes of a problem. It can help you see the different probabilities and calculate the final probability more easily. To use a probability tree, start by drawing a diagram with branches representing each possible outcome. Then, assign probabilities to each branch and follow the tree to calculate the final probability.
Breaking the Problem Down
If you have trouble solving the problem as a whole, try breaking it down into smaller parts. For example, if the problem involves drawing cards from a deck, calculate the probability of each event separately. This could include the probability of drawing a spade, the probability of drawing a black card, and the probability of drawing a spade given that the card is black. Then, combine these probabilities to get the final probability.
Question and Answer
Q: What is conditional probability?
A: Conditional probability is the probability of one event occurring given that another event has already occurred.
Q: How do you calculate conditional probability?
A: To calculate conditional probability, you need to consider the probability of Event A happening given that Event B has already occurred. This can be calculated using the formula P(A|B) = P(A and B) / P(B).
Q: What is a probability tree?
A: A probability tree is a visual way to represent the different outcomes of a problem. It can help you see the different probabilities and calculate the final probability more easily.
Q: How can you break down a Conditional Probability Example Problem?
A: If you have trouble solving the problem as a whole, try breaking it down into smaller parts. For example, if the problem involves drawing cards from a deck, calculate the probability of each event separately. Then, combine these probabilities to get the final probability.
Conclusion of Conditional Probability Example Problems
In conclusion, Conditional Probability Example Problems can be challenging, but with a little practice and some helpful tips, you can improve your understanding and solve these problems with ease. Remember to focus on understanding the concepts behind conditional probability and break the problem down into smaller parts if you get stuck. With these tools, you’ll be able to tackle any Conditional Probability Example Problem that comes your way.
Gallery
Mr Rouche’s Maths: Conditional Probability Trees
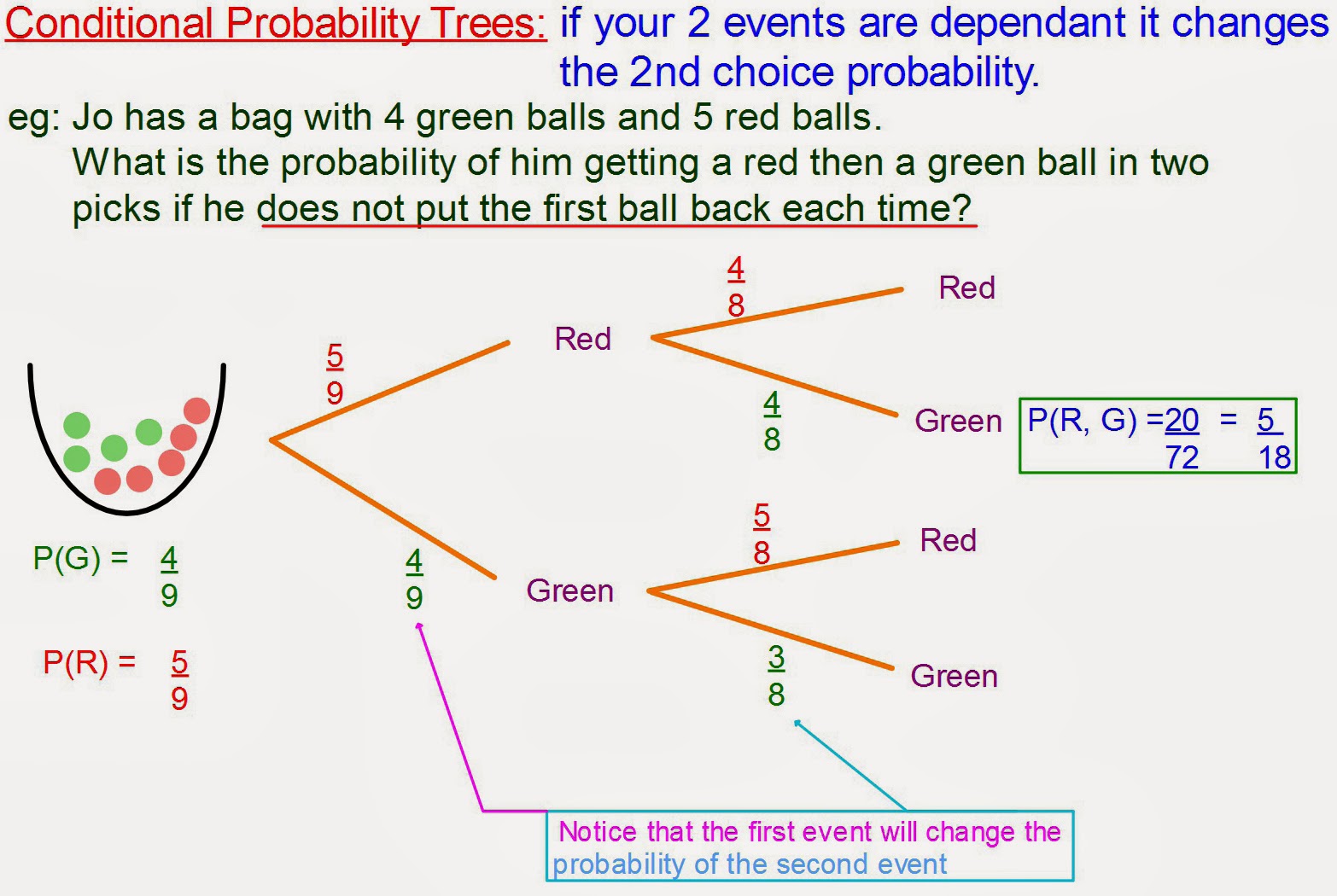
Photo Credit by: bing.com / conditional probability maths
Conditional Probability - Example 1 | Conditional Probability

Photo Credit by: bing.com / probability conditional contingency
Problems In Conditional Probability | Math | ShowMe
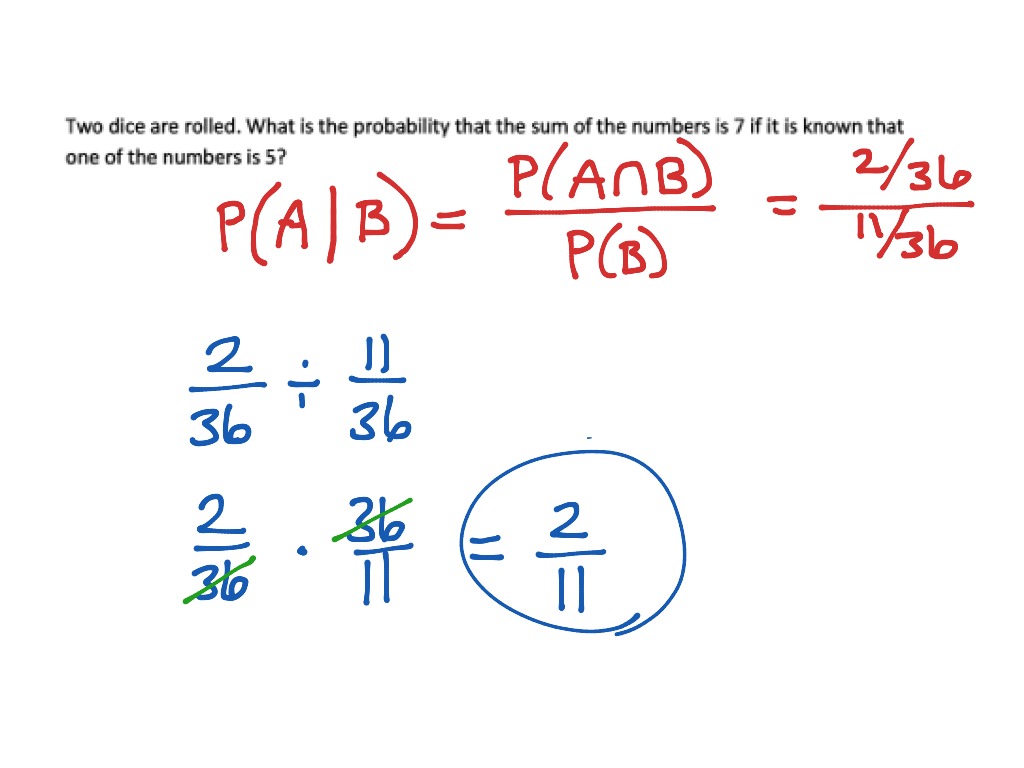
Photo Credit by: bing.com / probability conditional math problems
A Conditional Probability Video - YouTube

Photo Credit by: bing.com / conditional probability
Lesson Video: Conditional Probability | Nagwa

Photo Credit by: bing.com / probability conditional nagwa